|
|
|
|
 |
|
In the summer of 2024, Dutch citizens ranked climate change as the most serious problem facing the world. Just a few months later, they elected a national government that ran on a platform of pulling back its climate policies. ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Much of Europe sweltered in August 2025 as a heat dome spread across the continent, pushing peak afternoon temperatures to over 40 degrees C (104 degrees F) in France and Spain. Meanwhile, parts of Greece, Turkey and Albania battled historic and devastating wildfires as high temperatures scorch the land. ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
As hydrogen infrastructure is rolled out in the EU, refuelling stations must be distributed according to the same principle in all countries. But now a study from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, points to shortcomings in EU regulations. Using an advanced model, the researchers show that the distribution of refuelling stations may both be incorrectly dimensioned and lead to losses of tens of millions of euros a year in some countries.
...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
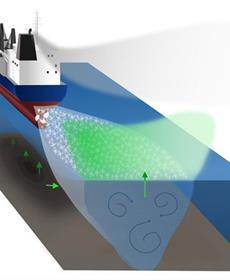
Ship traffic in shallow areas, such as ports, can trigger large methane emissions by just moving through the water. The researchers in a study, led by Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, observed twenty times higher methane emissions in the shipping lane compared to nearby undisturbed areas. Despite the fact that methane is a greenhouse gas that is 27 times as powerful as carbon dioxide, these emissions are often overlooked with today's measurement methods. ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Cellulose-based textile materials can make the clothing sector more sustainable. Currently, cellulose-based textiles are mainly made from wood, but a study headed by researchers from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden points to the possibility of using agricultural waste from wheat and oat. The method is easier and requires fewer chemicals than manufacturing forest-based cellulose, and can enhance the value of waste products from agriculture. ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
MSU is spearheading next-generation anaerobic digestion technologies that convert agricultural and food waste into renewable energy, recover nutrients and water, and support environmental sustainability across Michigan and the Great Lakes region. ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
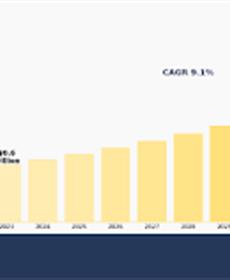
According to a new report published by Allied Market Research, the low carbon building market size was valued at $0.6 trillion in 2023, and is estimated to reach $1.3 trillion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2024 to 2033. ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
When two materials come into contact, charged entities on their surfaces get a little nudge. This is how rubbing a balloon on the skin creates static electricity. Likewise, water flowing over some surfaces can gain or lose charge. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have harnessed the phenomenon to generate electricity from rain-like droplets moving through a tube. They demonstrate a new kind of flow that makes enough power to light 12 LEDs ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Biomass is currently the EU’s largest renewable energy source, but climate strategies often focus on other energy sources. A comprehensive analysis, led by Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, now shows that biomass is crucial for Europe's ability to reach its climate targets, as it can be used to produce fossil-free fuels and chemicals and also enables carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere. If biomass were excluded from the European energy system, it would cost an extra 169 billion Euros per year – about the same as the cost of excluding wind power. ...more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Renting clothes can reduce the fashion industry's enormous environmental impact, but so far, the business models have not worked very well. The best chance of success is for a rental company to provide clothing within a niche market, such as specific sportswear, and to work closely with the suppliers and clothing manufacturers. This is shown by a study led by researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, which highlights the measures that can make clothing rental a success.
...more |
|
|